We have already analyzed in the previous post how we conducted the Electrifitty Study and the variables used in aerobic exercise.
In this post, we are going to delve into other variables, those related to body composition and DXA. It is worth noting that body composition and anthropometric measurements are, in addition to body image parameters, parameters of current health.
We know that a waist circumference above 90, or a fat % above 30 for men and 40 for women, is dangerous to overall health. That is why, in order to improve people’s body image, but also their health, we measure waist circumference, hip circumference, % body fat, and amount of visceral adipose tissue.
Other studies with WB-EMS
In previous studies, we have seen that training with electrostimulation improves fat % and body composition in healthy men.
We have also seen how a WB-EMS workout affects body fat and what decrease we were able to find.
On this occasion, we are going to compare two groups of people: some wearing the electrical stimulation vest and others without the electrical stimulation vest.
- The objective of the study: to learn more about and analyze the changes in body composition in the two groups.
- The hypothesis of the study: the application of EMS enhances the effects of exercise and helps to achieve better results.
Target audience of the study
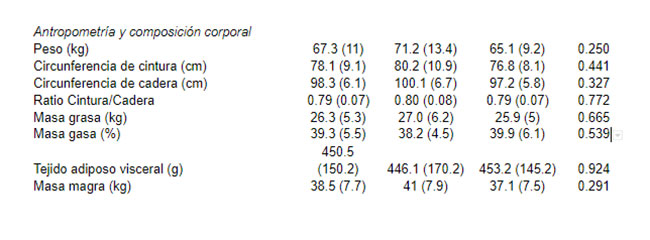
In the participants’ initial assessment, two main measurements were taken to indicate body composition and the distribution of fat, muscle and bone in the body:
- Anthropometry: Body weight and height were measured without shoes and in light clothing, using a scale and a measuring rod (model 799, Electronic Column Scale, Hamburg, Germany). Anthropometric measurements (i.e., waist and hip circumference) were determined following the protocol of the International Society for the Advancement of Kinathropometry (ISAK) (1). The waist-to-hip ratio (waist circumference/hip circumference) was calculated.
- Body composition: The assessment of body composition was completed before and after the intervention program with the use of a dual energy X-ray absorptiometry scanner (DiscoveryWi, Hologic, Inc, Bedford, MA, USA). The DXA analysis is the gold standard for measuring bone mineral density, although it also provides information on fat and muscle distribution.
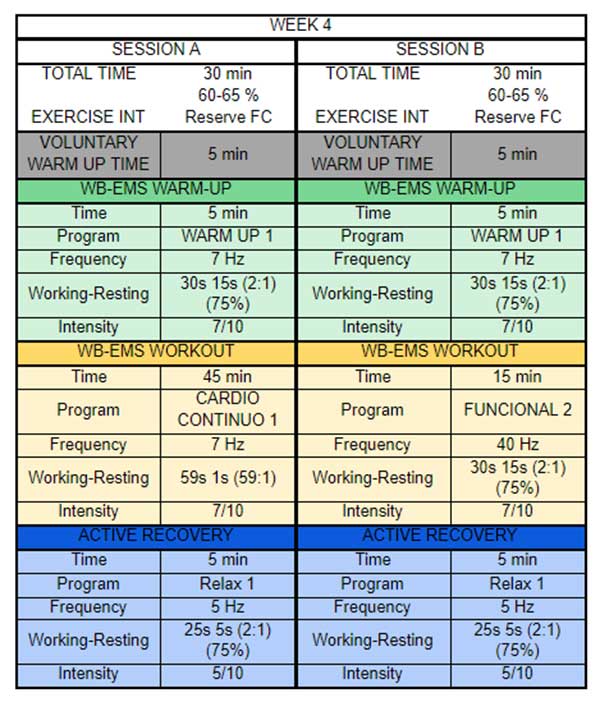
Training plan
The training plan that was carried out during this study is fully explained in this post.
To sum up, 4 training sessions per week were carried out for 4 weeks. The type of training was low-moderate intensity with continuous aerobic exercise. Participants trained at an intensity of 60-65% of their HR reserve, through cardiovascular exercise on and elliptical trainer or cycle ergometer.
On the other hand, participants in the WB-EMS group used two model workouts for each training day:
- One day the frequency used was 7 Hz.
- One day the frequency used was 7 Hz.
Two model days can be seen in the following table:
Study Results
As previously mentioned, we sought, on the one hand, to increase heart rate during training with the aim of increasing caloric expenditure and, on the other hand, to analyze the possible effects of the contraction produced by EMS on physical condition parameters.
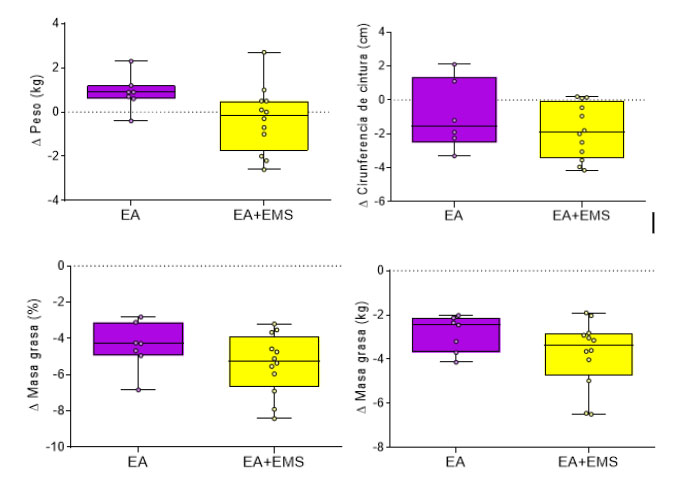
However, in this post, we are going to analyze the improvements obtained in the previously mentioned body composition parameters. For this purpose, we compared the changes obtained by each individual in each of the groups.
We can see in yellow the aerobic training group with WB-EMS; and in purple the group that only performed aerobic training. These boxes represent the mean values for each group.
Body composition and anthropometry
In terms of body composition, we see that there is a slight tendency to find a reduction in body weight, waist circumference and adipose tissue in the group training with whole-body electrostimulation.
As shown in the graph, the WB-EMS training group (yellow) is below the group that trained without WB-EMS (purple):
What does electrostimulation contribute to this process?
Once the results were analyzed, we were able to confirm that electrostimulation provides some benefits when it comes to physical exercise.
If we analyze these results more precisely, we do not find a statistically significant difference between the two groups; however, we can see in the images that there is a slight tendency towards improvement with the use of the electrostimulation suit.
The WB-EMS provides a higher energy expenditure in the session as it raises the heart rate and has an effect on body composition. At Wiems Lab, we continue to analyze the heart rate data in order to obtain an average for each of the participants.
Conclusion
The results of our study suggest that an aerobic training program with and without EMS is effective in improving anthropometric parameters and body composition in healthy young adults.
Although no statistically significant differences were observed between groups, a clinically relevant improvement in some variables under study was observed in the AE + EMS group. It could be said that this pilot study of very short duration (i.e. 4 weeks) may not yield significant differences due to lack of statistical power and, therefore, future studies with a larger sample size implementing a more specific periodization of the electrical parameters may be decisive in answering our question.
Unai Adrian Perez de Arrilucea
Wiems Lab Team







